I. SSO là gì?
SSO là một cơ chế xác thực yêu cầu người dùng đăng nhập vào chỉ một lần với một tài khoản và mật khẩu để truy cập vào nhiều ứng dụng trong 1 phiên làm việc (session).
Lợi ích của SSO
- Trước khi có đăng nhập một lần (SSO), một người sử dụng đã phải nhập các tài khoản và mật khẩu cho từng ứng dụng mỗi khi họ đăng nhập vào các ứng dụng khác nhau hoặc các hệ thống trong cùng một phiên (session). Điều này rõ ràng có thể tốn nhiều thời gian, đặc biệt là trong môi trường doanh nghiệp, nơi mà thời gian là tiền bạc nhưng thời gian là lãng phí bởi vì nhân viên phải đăng nhập mỗi khi họ truy cập vào một hệ thống mới từ máy tính của họ.
- SSO thường được thực hiện thông qua một module xác thực phần mềm riêng biệt hoạt động như một cửa ngõ vào tất cả các ứng dụng yêu cầu đăng nhập. Các module xác thực người sử dụng và sau quản lý truy cập vào các ứng dụng khác. Nó hoạt động như một kho dữ liệu chung cho tất cả các thông tin đăng nhập được yêu cầu. Ví dụ: Một ví dụ về một module SSO là hệ thống của Google khi mà người dùng chỉ cần đăng nhập 1 lần thì họ có thể sử dụng các dịch vụ của Google hay Yahoo mà không đòi hỏi đăng nhập 1 lần nữa như Gmail, Google Plus, Youtube….. Trong khi SSO là rất tiện lợi, một số nhận thấy nó như là một vấn đề an ninh của riêng mình.
- Nếu hệ thống SSO bị tổn thương, một kẻ tấn công có quyền truy cập không giới hạn cho tất cả các ứng dụng chứng thực của các module SSO.
- SSO thường là một dự án lớn cần lập kế hoạch cẩn thận trước khi thực hiện.
II. Thực hiện SSO
Hôm nay mình sẽ thực hiện SSO bằng cách sử dụng omniauth.
Mô hình cơ bản của oauth 3 chân
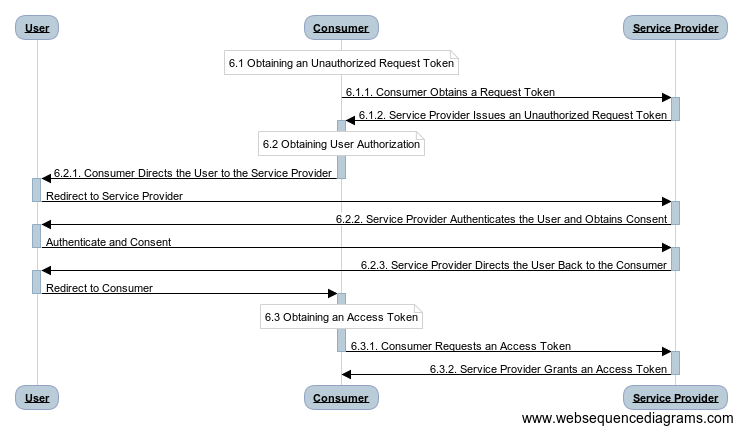
Đây chính là flow phổ thông cho mô hình oauth2 hiện nay. Client Credentials Flow sẽ được thực hiện thông qua việc redirect người dùng đến website của bên cung cấp dịch vụ, người dùng sẽ lựa chọn có đăng nhập hay không. Sau đó dựa vào redirect_uri mà "tôi" cung cấp trước đó cho provider sẽ redirect-back lại dịch vụ của "tôi", kèm theo một token đã được chứng thực. Sau cùng "tôi" sẽ sử dụng token đó như "chìa khoá" để truy cập vào profile.
Xây dựng provider
* Gemfile
gem "omniauth"
__* model/access_grant.rb__
class AccessGrant < ActiveRecord::Base
belongs_to :auth, polymorphic: true
belongs_to :client
before_create :generate_tokens
# Generate random tokens
def generate_tokens
self.code = SecureRandom.hex(16)
self.access_token = SecureRandom.hex(64)
self.refresh_token = SecureRandom.hex(16)
end
def self.prune!
delete_all(["created_at < ?", 3.days.ago])
end
def redirect_uri_for(redirect_uri)
if redirect_uri =~ /\?/
redirect_uri + "&code=#{code}&response_type=code&state=#{state}"
else
redirect_uri + "?code=#{code}&response_type=code&state=#{state}"
end
end
def self.authenticate(code, application_id)
AccessGrant.where("code = ? AND client_id = ?", code, application_id).first
end
def start_expiry_period!
self.update_attribute(:access_token_expires_at, Time.now + 1.minutes)
end
end* auth_controller.rb
class AuthController < ApplicationController
skip_before_action :authenticate_user_from_token!, :supplier_require_login, only: [:access_token, :authorize, :author]
skip_before_action :verify_authenticity_token, only: :access_token
def authorize
request = Rack::Utils.parse_query URI(params[:redirect_uri]).query
supplier_require_login and return
access_grand current_restaurant
end
def access_token
application = Client.authenticate(params[:client_id], params[:client_secret])
unless application
render json: {:error => "Could not find application"} and return
end
access_grant = AccessGrant.authenticate(params[:code], application.id)
unless access_grant
render json: {:error => "Could not authenticate access code"} and return
return
end
access_grant.start_expiry_period!
render json: {access_token: access_grant.access_token, refresh_token: access_grant.refresh_token, expires_in: Time.now}
end
def author
hash = {
provider: "sso",
id: authenticate_user_from_token!.id
}
render :json => hash.to_json
end
protected
def application
@application ||= Client.find_by_app_id(params[:client_id])
end
private
def authenticate_user_from_token!
if params[:oauth_token]
access_grant = AccessGrant.where(access_token: params[:oauth_token]).take
if access_grant.auth
access_grant.auth === Supplier ? supplier_log_in(access_grant.auth) : restaurant_log_in(access_grant.auth)
access_grant
end
end
end
def access_grand auth
AccessGrant.prune!
create_hash = {
client: application,
state: params[:state]
}
access_grant = auth.access_grants.create(create_hash)
redirect_to access_grant.redirect_uri_for(params[:redirect_uri]) and return
end
end* routes.rb
match "/auth/sso/authorize" => "auth#authorize", via: :all
match "/auth/sso/access_token" => "auth#access_token", via: :all
match "/auth/sso/auth" => "auth#author", via: :all
match "/oauth/token" => "auth#access_token", via: :allsessions_controller.rb
class SessionsController < ApplicationController
layout "login"
def new
end
def create
supplier = Supplier.confirmed.find_by(mail_address: params[:session][:mail_address])
if supplier && supplier.authenticate(params[:session][:password])
supplier_log_in supplier
return redirect_to(session[:prev_path])
else
flash.now[:danger] = "メールアドレスもしくはパスワードが間違っています"
render :new
end
end
def destroy
supplier_log_out
redirect_to login_path
end
end=> Ta đã xây dựng xong provider để authenticate cho supplier 2. Client connect to Provider Server
- Gemfile
gem "omniauth"
gem "omniauth-oauth2"- Tạo module sso lib/sso.rb
require 'omniauth-oauth2'
module OmniAuth
module Strategies
class Sso < OmniAuth::Strategies::OAuth2
option :client_options, {
site: CUSTOM_PROVIDER_URL,
authorize_url: "#{ENV['CUSTOM_PROVIDER_URL']}/auth/sso/authorize",
access_token_url: "#{ENV['CUSTOM_PROVIDER_URL']}/auth/sso/access_token"
}
uid do
raw_info["id"]
end
def raw_info
@raw_info ||= access_token.get("/auth/sso/auth.json?oauth_token=#{access_token.token}").parsed
end
end
end
end- config/enviroment.rb
# Load the Rails application. require_relative 'application' require "sso" # Initialize the Rails application. Rails.application.initialize! - config/initializers/omniauth.rb
Rails.application.config.middleware.use OmniAuth::Builder do
provider :sso, ENV["SSO_APP_ID"], ENV["SSO_APP_SECRET"]
end- sessions_controller.rb
class SessionsController < ApplicationController
layout "login"
def create
omniauth = env["omniauth.auth"]
auth = AccessGrant.find(omniauth["uid"]).auth
session[:supplier_id] = auth.id
flash[:notice] = "Successfully logged in"
redirect_to (session[:prev_path] || purchase_order_histories_path(q: {order_status_eq: "not_deliver"}))
end
def failure
flash[:notice] = params[:message]
end
def destroy
session.delete(:supplier_id)
@current_supplier = nil
redirect_to "/"
end
end* helpers/application_helper.rb
module SuppliersHelper
def supplier_log_in supplier
session[:supplier_id] = supplier.id
end
def current_supplier
@current_supplier ||= Supplier.find_by id: session[:supplier_id]
end
def supplier_log_out
session.delete :supplier_id
@current_supplier = nil
end
def supplier_logged_in?
current_supplier.is_a? Supplier
end
def supplier_require_login
unless current_supplier
respond_to do |format|
format.html {
redirect_to "/auth/sso"
}
format.json {
render :json => {error: "ログインしてください"}.to_json
}
end
end
end
end-
routes.rb
get "/auth/:provider/callback", to: "sessions#create" get "/auth/failure", to: "sessions#failure"





















Unpublished comment
Viết câu trả lời